A Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack is an attack in which one or more machines target a victim and attempt to prevent the victim from doing useful work.
RFC – 4732
What is DDOS?
DDOS is an acronym of Distributed Denial of Service. It is a type of Denial of Service attack. Attacker’s motivation may vary from preventing the victim from doing useful work to using DDOS as a deception to infiltrate sensitive data from victim. No matter what the attacker’s motivations are we are here to defend our network.
DDOS attack types
First of all, there is no industry standard for DDOS attack categorization. But based on the similarities and characterizations of the attacks we can categorize them in to 3 main type.
- Volumetric attacks
- Protocol attacks
- Application layer attacks
Before we go any further i would like to share a chart that shows the attack types and their respective DDOS solution. I am not gonna deep dive into the specific attack types and their respective mitigation strategies but you may use the below chart as a starter point.
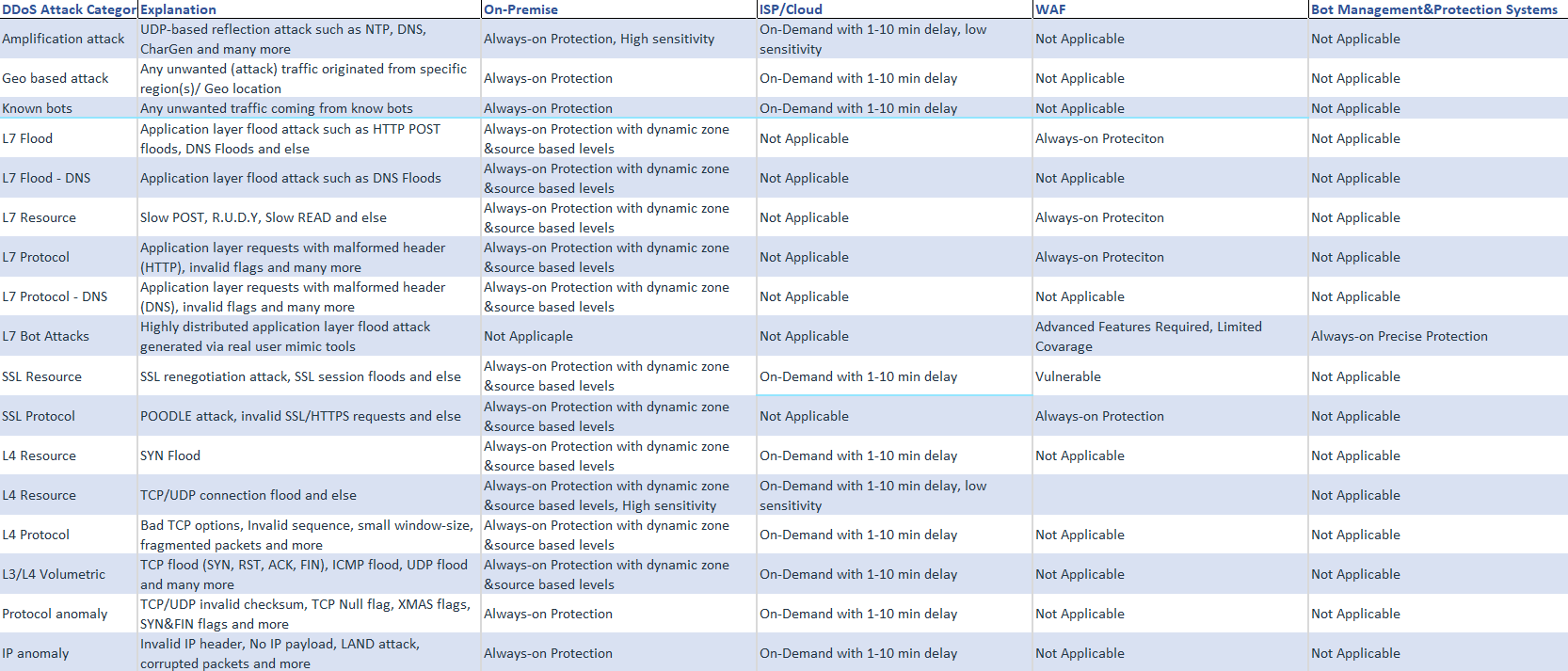
Above chart is created by Fatih Okumus
Volumetric attacks
The goal of this type of attacks is comsuming your bandwith. In volumetric attacks, the attacker sent huge amount of traffic to victim’s system. Traffic may come from either amplified or from a botnet. Either way its goal is same. Generally this type of attacks are mitigated on the cloud scrubbing services or in the ISP layer. Magnitude of the attacks are measured in bits per second (Bps). Biggest ever Volumetric attack targeted to GitHub website so far. It reached a magnitude of 1.35Tbps in its peak and lasted 20 minutes according to Cloudflare.
Protocol attacks
The goal of a protocol attacks is consuming the physical devices resources by leveraging the weaknesses of layer three or layer 4 protocols. SYN Flood , UDP Flood or Ping of Death attacks are some well known example to protocol attakcs. As seen from the above chart protocol attacks mitigating on ISP / Cloud services side or on-premise ddos solution. Best practice to avoid service disruption is using both ISP / Cloud solutions and on-premise DDOS device solutions together. Key point here is on-premise devices are in always-on protection mode. This gives the defender side a head start. You can mitigate from the very beginning of the attack thus damage will be minimum to none. Its magnitude is packets per second (pps).
Application layer attacks
Finally application layer attacks, also known as Layer 7 attacks. The goal of a Layer 7 attack is consuming the web server’s resources. This type of attack is generally starts from client side. A request is sent to web server and this request has to be answered from the service’s web server. Every time client makes a request server generates a response. In this request response life-cycle attacker abuses requests. As from the sectoral common sense this type of attacks are hard to defense because of its nature. It is hard to flag a request as attack. While you ,as a security engineer, are securing your assets you also do not have to interrupt normal client requests. Best mitigation strategy against layer 7 attacks is using both on-premise ddos device and a Web Application Firewall solution. Some cloud DDOS protection service providers also offer WAF.
Final words…
To sum up DDOS attacks exploits and targets different resources. As a result, solution must be layered and custom tailored. No matter how you targeted the final goal from the attackers perpective is causing a service disruption. Lastly some resources says that there is a fourth category; Multi vector attacks. It is a mixture of the above attacks.

